Crypto Mining Explained: What is Crypto Mining and How It Functions
2025/08/18 09:27:02

You must hear of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, and you may even know that they are “mined.” But what does that really mean? It’s not about shovels and dirt. Instead, crypto mining is a digital process that powers decentralized networks like Bitcoin.
At its core, crypto mining is the process of using powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems. These problems are designed to be difficult to solve but easy for the network to verify. When a miner solves the problem, they get to add a new "block" of verified transactions to the blockchain—a process known as Proof of Work (PoW). It’s like a global race where thousands of computers are competing to be the first to complete a digital puzzle, thereby earning the right to stamp the next page in a global ledger.
The Twofold Purpose of Mining
Mining serves two essential functions that maintain the health and security of a blockchain network:
-
Securing the Network: By requiring vast amounts of computational power, mining makes it incredibly difficult and expensive for a malicious actor to manipulate the network. It would take a tremendous amount of energy and resources to alter a single block, as a miner would have to redo all the work of the miners who came after them.
-
Issuing New Coins: Mining is the only way new cryptocurrency enters the ecosystem. As a reward for their work, the first miner to solve a block receives a predetermined amount of newly minted coins plus any transaction fees associated with the block. This is a fundamental concept behind Bitcoin mining principles and other PoW cryptocurrencies.
From CPUs to Mining Pools: The Evolution of Mining
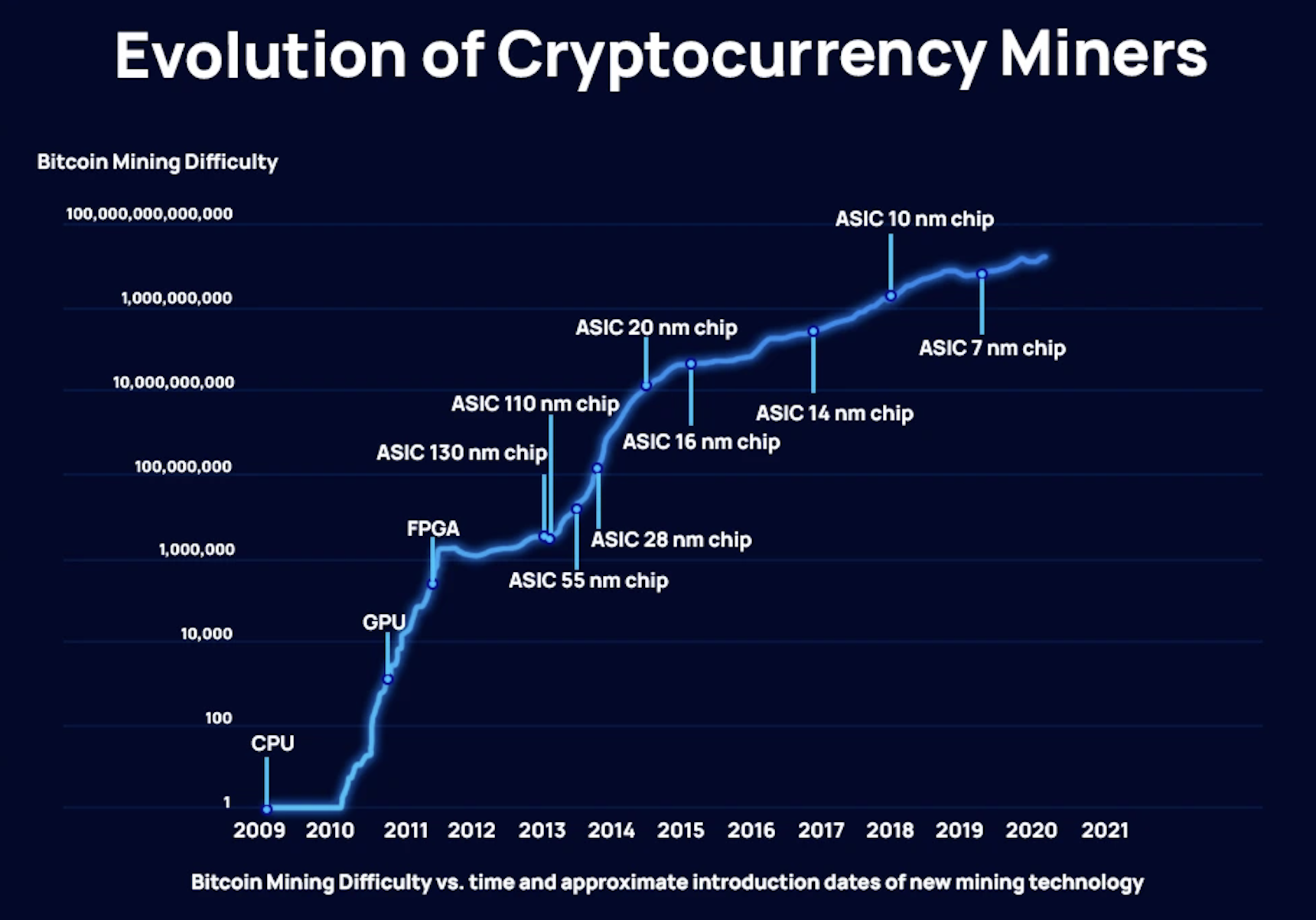
Credit: CoinDesk and ASICmarketplace
The method of mining has evolved dramatically over the years.
-
Early Days (CPU/GPU Mining): At the beginning, anyone with a standard computer could participate. Miners used their Central Processing Units (CPUs) and later their Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) to mine. While tutorials for GPU mining can still be found, this method is no longer profitable for major cryptocurrencies due to the immense competition.
-
The Rise of ASICs: As mining difficulty increased, specialized machines known as Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) emerged. These are custom-built devices designed for one purpose: crypto mining. They are far more efficient than CPUs or GPUs, making them the standard for large-scale operations.

Image: bitstamp
-
Joining a Mining Pool: Today, the chances of an individual miner with a single machine solving a block on their own are slim to none. This gave rise to mining pools, where thousands of miners combine their computational power (hash rate) to increase the probability of successfully finding a block. When a pool solves a block, the reward is split among all participants based on the amount of hash power they contributed. If you’re wondering how to choose a mining pool, it's a popular and practical way to get started. You can learn more about how they work by visiting a platform like https://www.kucoin.com/mining-pool.

A Step-by-Step Guide of the Mining Process
So, how does it all work? Let's break it down step-by-step.
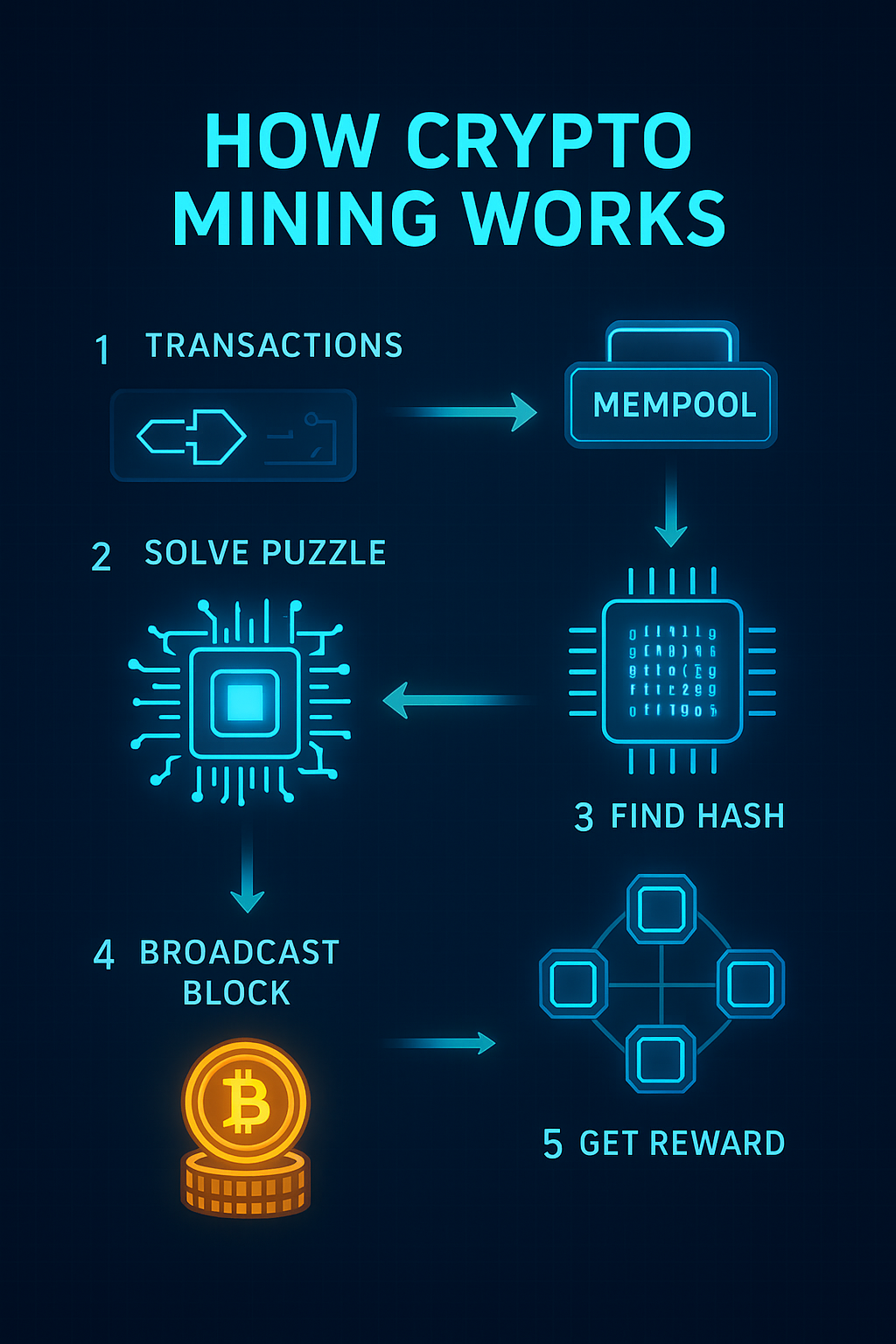
At its core, mining is a race to create a new "block" of transactions and add it to the blockchain. Here’s a simplified look at the process.
-
Gathering Transactions The process begins when new transactions are broadcast to the network. For example, when you send Bitcoin to a friend, that transaction is publicly announced but not yet confirmed. It sits in a waiting area called the "mempool" with thousands of other transactions, waiting for a miner to pick it up.
-
The Race to Solve the Puzzle Each miner (a computer or a collection of computers) competes to be the first to solve a complex cryptographic puzzle. A miner's computer takes the unconfirmed transactions, combines them with a special number called a "nonce," and applies a cryptographic function (a hash algorithm) to the data. This process generates a long string of letters and numbers called a "hash."
-
Finding the Right Hash The goal is to find a hash that meets a specific target set by the network. Think of it like a lottery: the miner's computer is repeatedly guessing different nonces, generating a new hash with each guess. It’s a brute-force guessing game, and the computer's "hash rate" measures how many guesses it can make per second. The first miner to find a hash that meets the network's difficulty target wins the race. For details, visit Tutorial of BTC Hashrate Connecting >>>
-
Broadcasting the Solution Once a miner finds the winning hash, they instantly broadcast their solution (the new block) to the entire network. Other miners then verify the solution. This is quick and easy for them to do. Once verified, the new block of transactions is permanently added to the blockchain.
-
The Reward The successful miner is rewarded with newly minted cryptocurrency (the "block reward") and all the transaction fees from the transactions included in that block. This reward is the primary incentive for miners to contribute their computational power to the network.
The High Cost of the Mining Journey
While the prospect of earning cryptocurrency is enticing, the journey is not without its challenges. The question, "Is home mining feasible?" often leads to a quick reality check. The main hurdles are:
-
Hardware Costs: Professional mining machines can be expensive, requiring a significant initial investment.
-
Electricity Consumption: The immense power required to run mining rigs around the clock translates to huge electricity bills. In fact, electricity is often the single biggest operational expense.
-
Competition and Difficulty: As more miners join the network, the difficulty of the mathematical problems automatically increases. This makes mining profitability calculation a complex task, as you must factor in the constantly changing network difficulty and the price of the cryptocurrency.
Looking Ahead: PoW vs. PoS
The energy consumption of Proof of Work (PoW) has led some blockchains to explore alternative methods. One notable alternative is Proof of Stake (PoS), where the network is secured by validators who "stake" or lock up their existing coins as collateral. This method requires significantly less energy and is viewed by some as a more sustainable future for cryptocurrency.
Despite these new models, crypto mining remains a cornerstone of the original decentralized vision. It is the complex, energy-intensive process that ensures the integrity and security of many of our most valuable digital assets. It’s a journey that combines technology, economics, and a whole lot of computing power to create a truly decentralized financial system.

