Bitcoin Mining Guide for Beginners: How Does BTC Mining Work and Is It Still Profitable?
2025/08/19 09:30:02
For many, the term "Bitcoin mining" conjures up a mysterious and complex image of computers working day and night to "mine" virtual gold coins. But the true nature of Bitcoin mining is far more profound; it's not just how new coins are created, but also the fundamental cornerstone of the entire Bitcoin network's security.

This article will use simple, easy-to-understand language to take you on a deep dive into the true meaning of Bitcoin mining, the Proof-of-Work (PoW) principle behind it, and how an average person can get involved.
1.What Exactly Are We "Mining"?
Bitcoin mining isn't about digging for virtual money; it's a global digital competition. Miners use specialized computer hardware (mining rigs) to compete against each other, performing a massive number of hash calculations to solve a complex mathematical puzzle set by the Bitcoin network.
This puzzle can be thought of as a race to find a number that, when calculated with a block of pending transactions, produces a hash value that begins with a certain number of zeros. It’s a purely computational race with no shortcuts.
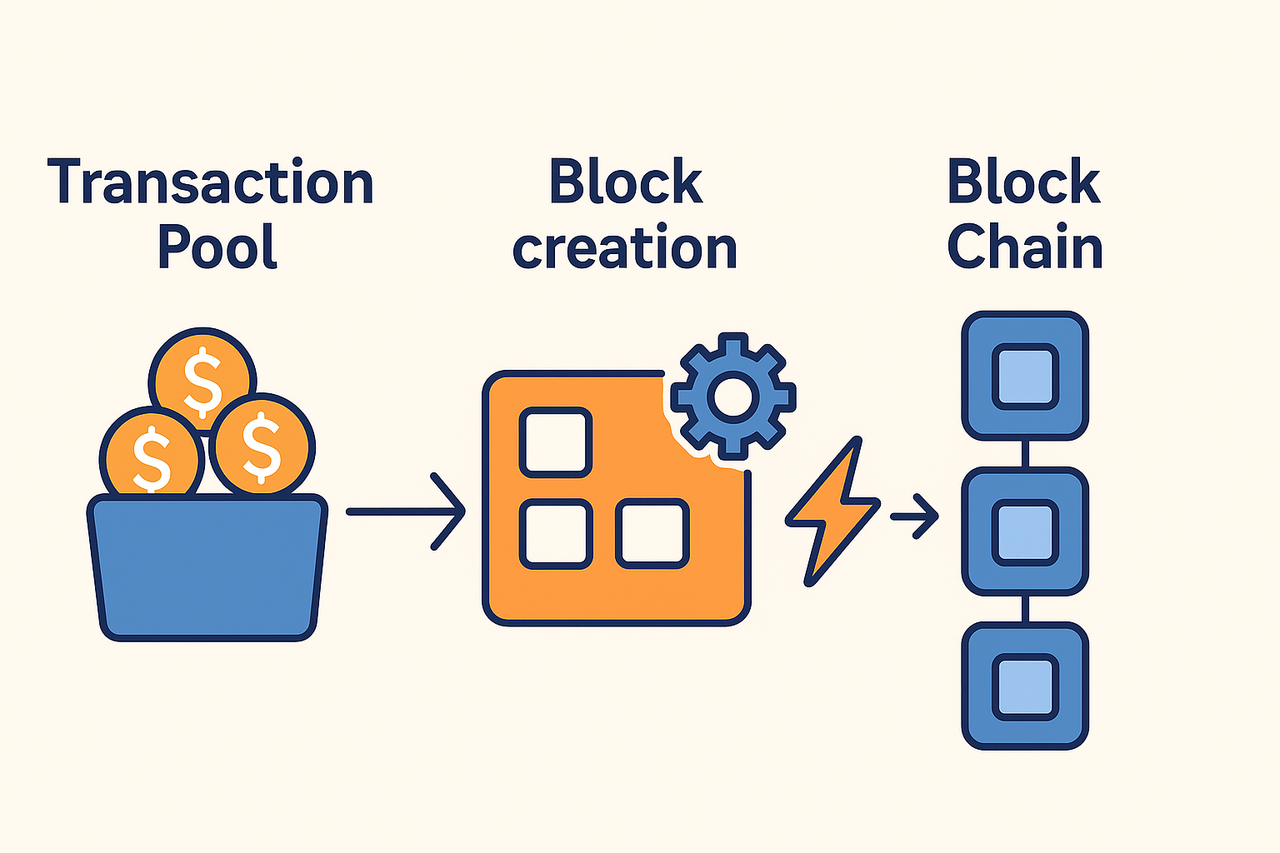
2.The Core Principle: Proof-of-Work (PoW)
The core mechanism behind Bitcoin mining is called Proof-of-Work (PoW). It ensures that the mining process is fair and secure. The PoW mechanism works like this:
-
Gathering Transactions: The miner's computer collects unconfirmed transactions from the network.
-
Creating a Block: These transactions are bundled into a block, along with a random number (called a "nonce").
-
The Puzzle Race: Miners continuously change this random number and run a hashing algorithm (SHA-256) until they find a valid hash that meets the network's requirements.
-
Earning Rewards: The first miner to find the correct hash earns the right to add the new block to the blockchain, and is rewarded with newly minted Bitcoin (the block reward) and the transaction fees.
This "work" requires significant computing resources and electricity, which is why the name Proof-of-Work is so fitting. This high cost is what makes it economically unfeasible for malicious actors to attack the network, thus guaranteeing its security and decentralization.
3.The Economics of Bitcoin Mining: Costs, Competition, and the "Halving"
Mining isn't just a technical endeavor; it's a business. Its profitability is determined by several key factors:
-
Mining Costs: The main costs are hardware (such as the Antminer S19/S21, which can cost thousands of dollars) and electricity. Miners must continuously upgrade their rigs and seek out cheap power sources to remain competitive.
-
Hash Rate and Mining Difficulty: The combined computing power (hash rate) of all miners globally determines the network's total hash rate. To maintain a consistent block generation speed of roughly every 10 minutes, the Bitcoin network automatically adjusts the mining difficulty. When the total hash rate increases, the difficulty also rises, and vice versa.
-
Bitcoin "Halving": This is the most crucial event for the network. The mining block reward is cut in half every 210,000 blocks (roughly every four years). In 2024, Bitcoin underwent its fourth halving, reducing the block reward from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC. This means miners have a much harder time earning new coins, directly impacting their profitability. Historically, each halving has been followed by a major bull run, as the supply of new coins entering the market is reduced.
4.How to Participate in BTC Mining? A Full Breakdown of Three Methods
If you're interested in Bitcoin mining, here are the most common ways to get involved:
-
Individual Mining (High Barrier):
-
This is the traditional method, requiring you to purchase an expensive ASIC mining rig and deal with high electricity costs, noise, and heat. Due to the massive global hash rate, a single miner's chance of solving a block is extremely low. For example, after the 2024 halving, a single new-generation rig could take years to even break even.
-
Joining a Mining Pool (The Mainstream Method):
-
This is the most common and effective way to mine today. A mining pool is a collective of miners from all over the world who combine their hash power. When any member of the pool finds a block, the reward is distributed proportionally to each miner's contribution. Well-known pools like F2Pool and AntPool account for a large portion of the global hash rate. You can also join a reputable exchange-run pool, such as the KuCoin Mining Pool:https://www.kucoin.com/mining-pool.
-
Pros: Stable income, diversified risk.
-
Cons: Requires paying a small fee to the pool.
-
-
Cloud Mining (The Simplest Method):
-
This is the easiest option for non-technical individuals. You don't need to buy or maintain any hardware; you simply rent computing power from a cloud mining service provider.
-
Pros: Easy to use, no hardware risks or maintenance costs.
-
Cons: Often involves hidden fees and a risk of the provider shutting down, so choose carefully.
-
5.The Future Trend of Bitcoin Mining: More Professional, More Sustainable
With increasing competition and the approaching halvings, Bitcoin mining is becoming more professional and large-scale. Massive mining farms are replacing home operations, often located in regions with cheap electricity and cool climates.
Additionally, to address energy consumption and environmental concerns, more and more mining companies are using renewable energy sources (such as hydro, wind, and solar). This not only lowers costs but also enhances Bitcoin's reputation as a "green" asset. For example, some farms are built directly near hydroelectric dams or use waste natural gas for power.

Conclusion
Bitcoin mining is the lifeline that sustains the Bitcoin network. It is not just a means of making money, but a great invention that ensures network security and achieves decentralized consensus. For the average investor, the most sensible approach is to understand its principles, choose a reliable way to participate, and recognize that it is a field with both high risks and high rewards.

